
Goat Buttes and Century Lake from the Lookout Trail.
From Sunday’s run in Malibu Creek State Park.
Some related posts: Century Lake, Dam and Gorge on Malibu Creek, Malibu Creek State Park Shadow & Sun, Century Lake Morning

Goat Buttes and Century Lake from the Lookout Trail.
From Sunday’s run in Malibu Creek State Park.
Some related posts: Century Lake, Dam and Gorge on Malibu Creek, Malibu Creek State Park Shadow & Sun, Century Lake Morning

Benefiting from the cool ocean air that flows into Malibu Canyon, the afternoon shadows of Goat Buttes, their north-facing aspect, and the sustaining waters of Malibu Creek and Century Lake, the 100-year-old coast redwoods in Malibu Creek State Park appear to be thriving.

Coast redwoods are not endemic to Southern California. According to Los Padres Forestwatch, the southernmost stand of naturally-occurring coast redwoods is on the coast about 200 miles north of Malibu Creek State Park in an area of Los Padres National Forest designated the Southern Redwood Botanical Area.
Numerous redwoods have been planted in Southern California, and not all of them are doing well. A reprint of the 2004 article “What’s up with the redwoods?” by James Downer, originally available as a resource link on the Urban Forest Ecosystems Institute website, discusses a dramatic decline in coast redwoods planted in Ventura County and describes some of the problems facing this wonderful tree.
Perhaps the Malibu Creek State Park redwoods have a better chance of surviving, and naturally occurring or not, will be enjoyed by Park visitors for centuries to come.
From this morning’s trail run in Malibu Creek State Park.
Some related posts: The Malibu Creek State Park Redwoods Are Dying, Malibu Creek State Park Redwoods: Fighting the Drought

These unusual clouds are a complex of lenticular clouds to the north-northeast of Mt. Pinos, photographed this morning from near Mt. Abel. They were produced by strong south-southwesterly winds blowing across the east-west oriented Emigdio and Tehachapi mountain ranges, north of Los Angeles. Here’s another view of these clouds from near the summit of Mt. Pinos.
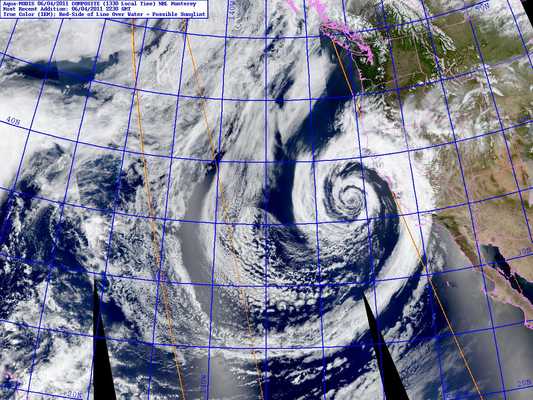
The winds were associated with the circulation of an unseasonably strong low pressure system off the California coast. The storm system has resulted in measurable rain as far south as Santa Barbara County, and new rainfall records for the date were set in San Francisco, Paso Robles and Santa Maria.

The photographs were taken during a blustery out and back trail run from Mt. Pinos to Mt. Abel on the Vincent Tumamait Trail in the Chumash Wilderness. At the start of the run, the temperature at the Chula Vista trailhead (8400′) on Mt. Pinos was a chilly 39°F. In exposed areas the wind speed was 20-25 mph with gusts to around 50 mph.
Other than the potential for deadfall, the wind wasn’t too bad in the trees. The Vincent Tumamait Trail was in the best condition I’ve seen in years.
Update June 6, 2011. The low that was off the Central California coast Saturday and most of Sunday and an associated cold front set a new rainfall record for June 5 at Santa Barbara Airport, and produced a few sprinkles and showers in the Los Angeles area.
Some related posts: Mountain Weather, Lenticular Wave Clouds, Mt. Pinos – Mt. Abel Out & Back

Scorched Jeffrey Pines on the South Side of Waterman Mountain
It was very odd to run up the Mt. Waterman Trail on the Sunday of a 3-day Memorial Day weekend, and see no one. And hear nothing, except the wind in the trees, the distant call of a jay, and the periodic drone of a contractor’s truck working on the highway. That’s because — surprise, surprise — Angeles Crest Highway was closed a little east of Three Points and on to Islip Saddle. CalTrans Road Conditions had only listed the Winter closure from Islip Saddle to Vincent Gap. Based on the number of cars parked at the closure, not many people knew about it.
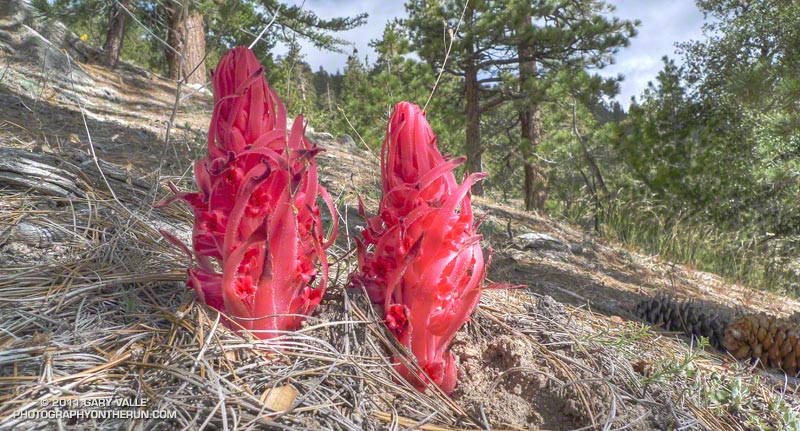

I hadn’t known about it until I saw the Ranger’s truck and closed gate from the Pacific Crest Trail. I was doing a loop from Three Points up the PCT to the Burkhart Trail, then up to Buckhorn, over Mt. Waterman, and back down to Three Points. Part of this loop — from Mt. Waterman to Three Points on Trail 10W04 — had just reopened, and like last weekend I wanted to see how recovery from the 2009 Station Fire was progressing.
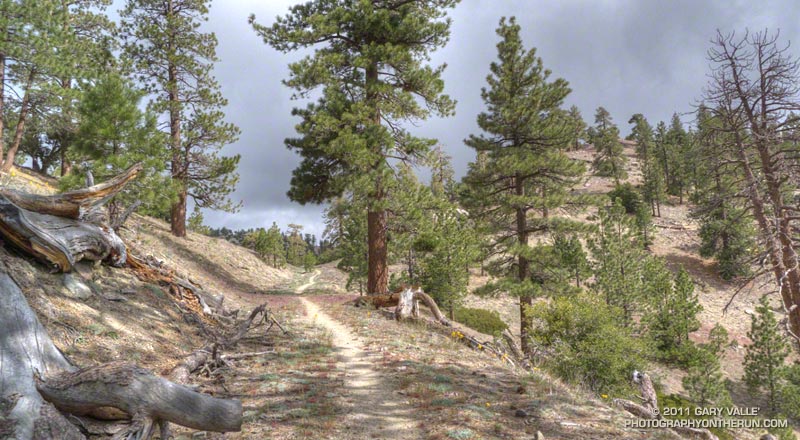

The conditions were much better on this loop, than last week’s. Although within the initial Station Fire Closure area, and closed for eight months, 11 of the first 13.5 miles of the loop were not burned in the Station Fire. This mostly unburned stretch opened in late May 2010 and is described in the post Three Points to Waterman Mountain, the Long Way.

The remaining six miles of the loop, which winds in and out of the shallow canyons on the south side of Mt. Waterman, was in the burn area. Conditions along the trail appeared to generally correspond to BAER burn severity maps and images. At the higher elevations, fingers of the fire had run up the steep slopes, burning understory and scattered Jeffrey pines and incense cedars, while leaving other areas untouched.
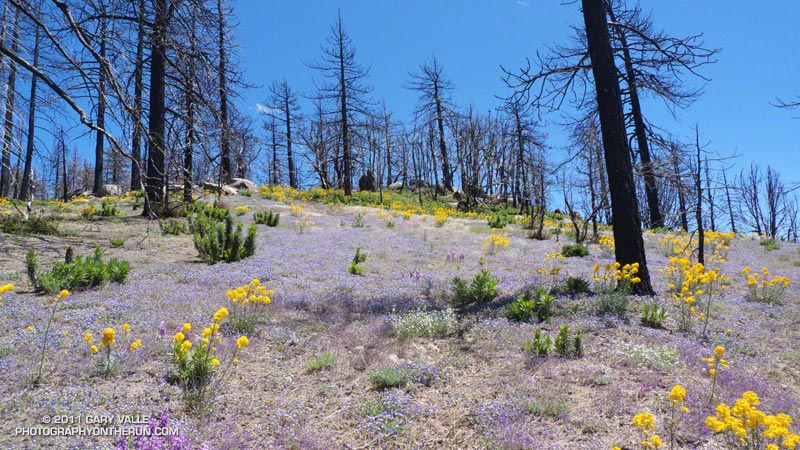

At lower elevation, particularly in the chaparral and pine at the head of the north branch of Devils Canyon, the fire effects were more severe. The chaparral is recovering, but numerous Coulter and Jeffrey pines appeared to have been killed, and their replacement will be a slower process. This area is traversed by the last two miles of Trail 10W04, leading to Three Points.
There was very little, if any, damage from runoff and the trail was generally in good shape. The trail was slightly overgrown in spots, particularly at lower elevation, but was nothing like the Gabrielino Trail between Switzer and Red Box. There was some Turricula (Poodle-dog bush) at lower elevation, but for the most part it was fairly easy to avoid. Some pine needle covered sections of trail were indistinct, but it was like that before the fire.

From a trail running perspective, it is still a very “runnable” course with varied terrain and much to see and enjoy. Cooper Canyon Falls is very short side trip from the PCT’s junction with the Burkhart Trail. The side trip to the summit of Mt. Waterman (8038′) adds about two miles to the loop.
Some related posts: Three Points – Mt. Waterman Loop, Three Points Loop Plus Mt. Waterman

I knew Poodle-dog bush* was a common fire follower, but had never run or hiked through a burn area where it was abundant. Wow, it was everywhere on the Red Box – Bear Canyon – Gabrielino Loop last Saturday, and particularly dense on sections of the Gabrielino Trail between Switzers and Red Box. It appears to be one of the most common fire-followers in the Station Fire burn area, and likely plays an important role in the recovery process.

Gland-tipped hairs on the plant secrete a sticky substance that causes a rash “like poison oak” in sensitized persons. I thought I wasn’t sensitive to the plant, because I had brushed against the leaves of Poodle-dog bush before without reacting to it. This time my exposure was repeated, frequent, and prolonged; and the leaves were heavily coated with exudate. At the end of the loop my legs and forearms were coated with a thick layer of resinous brown gunk that would not wash off with water.

By the time I had finished the run, talked to some people at Red Box, and driven home, 2-3 hours had passed. Tecnu helped remove the resinous goo, but as I would discover a couple of days later, it did not prevent me from getting the rash.
My reaction to Poodle-dog bush was quite a bit different than what I’ve experienced with poison oak. A blotchy red rash developed on my arms and legs Monday, about 48 hours after exposure. After another 24 hours I thought the rash was going away, but it was actually morphing into a more widespread and uniform inflammation that was similar to bad sunburn — a very itchy sunburn. There was some swelling and edema, particularly on my ankles. In the areas that had the most contact with the Poodle-dog bush, primarily my shins and around my knees, there was some blistering. The blisters were small, perhaps 1/16 inch in diameter or less.

Most of the blisters were gone by Thursday afternoon, and since then the inflammation has been slowly subsiding. Although very itchy and annoying at times, it has not been debilitating. An equivalent exposure to poison oak would have been much more severe. However, in my case an underlying irritation or sensitivity has lingered for some time after the visible reaction dissipated. It seems like it will probably take a few more days for the reaction to completely resolve. We’ll see!
Update July 12, 2011. My reaction to Poodle-dog bush cleared after about two weeks. A running friend who recently did some trail work removing Turricula on the Kenyon Devore Trail sent this photograph of a blotchy red rash that developed on his forearm. He first noticed a reaction four days after doing the trail work, and the photograph was taken 10 days after exposure. As in my case, several hours later he commented that the blotchy rash had merged into a more general inflammation with swelling.

Research has found the dermatitic agents in the Poodle-dog bush exudate are “phacelioids,” hydroquinone based compounds structurally related to poison oak/ivy urushiols, but not as active. In one study the amount of the phacelioids in Poodle-dog bush required to produce a qualified reaction was 100 times that required for a component of urushiol from poison ivy — 170 µg vs 1.6 µg.
It is also noted that in place oxidation of hydroquinone based phacelioids is likely necessary to interact with the proteins of the skin and produce a reaction. This (and common sense) suggests that leaving the Poodle-dog bush exudate on your skin for several hours (like I did) is probably a bad idea.
For more information see:
Contact Dermatitis From Eriodictyon parryi: A Novel Cause of Contact Dermatitis in California. Christopher D. Czaplicki, Wilderness & Environmental Medicine, 2013; 24(3):253–256
Prenylated Phenolics that Cause Contact Dermatitis from Glandular Trichomes of Turricula parryi. G. W. Reynolds, P. Proksch, E. Rodriguez, Planta Medica, 1985; 51(6): 494-498
Unusual contact allergens from plants in the family Hydrophyllaceae. G. W. Reynolds, W. L. Epstein, E. Rodriguez, Contact Dermatitis, 1986; 14:39-44
The book Poisonous plants of California by Thomas C. Fuller, Elizabeth May McClintock (1986) describes a 1941 incident in which hairs from old flowering stalks “easily broken from the stems” caused a rash, but flowering plants the previous year did not.
*The taxonomic name for Turricula parryi (Poodle-dog bush) has changed to Eriodictyon parryi. The Jepson Manual: Vascular Plants of California, Second Edition (2012) has returned Turricula to the genus Eriodictyon, as originally described by Gray. According to the Wikipedia entry for Turricula (April 11, 2012), “… molecular phylogenetic analysis carried out by Ferguson (1998) confirms that Turricula should be treated as a separate genus within a clade (Ferguson does not use the term “subfamily”) that includes Eriodictyon, and also the genera Nama and Wigandia; Eriodictyon is the genus to which Turricula is closest in molecular terms, and is its sister taxon.” I use “Turricula” and “Poodle-dog bush” interchangeably as a common name.
Related post: Getting Over Poodle-dog Bush Dermatitis and these additional posts.

Most chaparral plants thrive in years in which we have above average rainfall, including poison oak. This poison oak is on the Phantom Trail in Malibu Creek State Park.
From Sunday’s trail run.