Perhaps the only thing more difficult than forecasting rain in Los Angeles is forecasting snow in Los Angeles. A NWS Winter Weather Advisory issued Friday evening for the Santa Monica Mountains Recreation Area forecast the snow level to drop overnight from above 3000′ to between 1000′ and 1500′. Snow accumulations from 1 to 3 inches were expected.
When getting ready for a run on those searing 100 degree days at Ahmanson Ranch, I look longingly at the Lasky Mesa snow photos from 1943 displayed in the information kiosk at the Victory Trailhead. Would that rare snow scene be repeated? If so, I wanted to see it. I’m a skier from way back, but snow in the hills near my Los Angeles area home is an altogether different thing.
Last weekend it looked like we might get some snow on the higher parts of Rocky Peak Road for the Bandit 15K/30K/50K trail runs. There was some snow on Oat Mountain, but not down to Rocky Peak. The Rocky Peak area is about 500′-1000′ higher than Lasky Mesa, so snow there isn’t quite as rare. The last time I ran in the snow on Rocky Peak Road was in December 2008, and before that in March 2006.

Snow is an iffy thing in the Los Angeles area. The ocean is the dominant moderating influence. Storms generally bring in air warmed by the ocean, and the coldest air often doesn’t move in until after most of the precipitation has ended. To get low elevation snow, the timing and conditions have to be just so. Whether it snowed or not, it looked like it would be an interesting weather day, so I planned to get up early and do a morning run.
At dawn the lack of snow on the local foothills made it plainly evident that all the ingredients required for very low elevation snow had not come together. Overnight there had plenty of snow — four feet of it at 7500′ at Mt. Baldy — just not much low elevation snow. (Later in the day post frontal convection would produce some isolated showers of icy snow in the east San Fernando Valley and La Crescenta.)
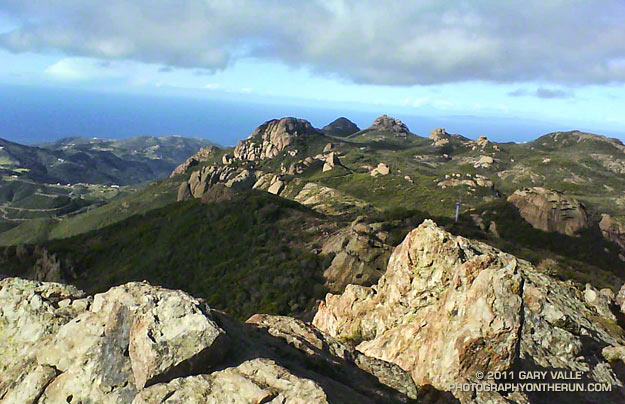
On the off chance there had been a dusting of snow at the higher elevations of the Santa Monica Mountains, I decided to do the Mishe Mokwa – Backbone Trail loop and check out the conditions on 3111′ Sandstone Peak, the highest peak in the range.
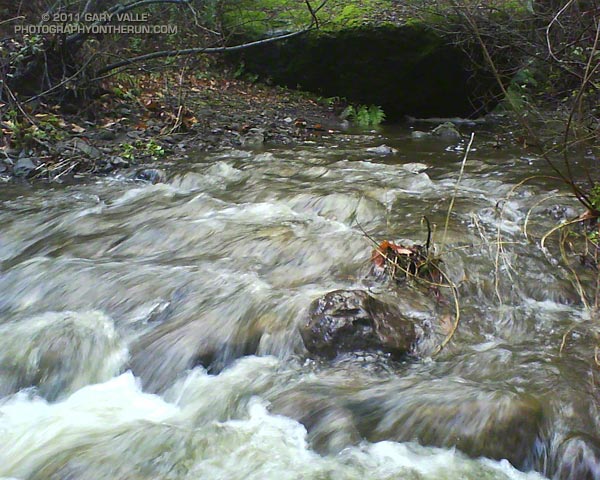

What a great morning for a trail run! When I started the loop, it was partly cloudy and the temperature at the Mishe Mokwa trailhead (el. about 2100′) was a chilly 37 degrees. The ground was soaked, and the chaparral wet with rain. Streams filled every gulch and gully, and the gorge along Echo Cliffs roared with runoff. Level sections of the Mishe Mokwa Trail were nearly one continuous puddle. Two creek crossings — one at Split Rock and another near the Backbone Trail — were wide enough to require wading.
Running the rocky trail with care, it took a little under an hour to reach the Backbone Trail junction. As I puffed up the trail toward Sandstone Peak, each exhalation was visible. I found myself reveling in each frosty cloud, as it would hang briefly in the morning sun, and then dissipate.
Although I could see no snow, it was cold enough that I thought there was a chance there might be some residual snow in the shade on the northwest side of the peak. Rounding the corner, I started up the makeshift stairs at the beginning of the spur tail leading to the summit. On top it was cold, windy, wet and spectacular, but — sigh — there was no snow.
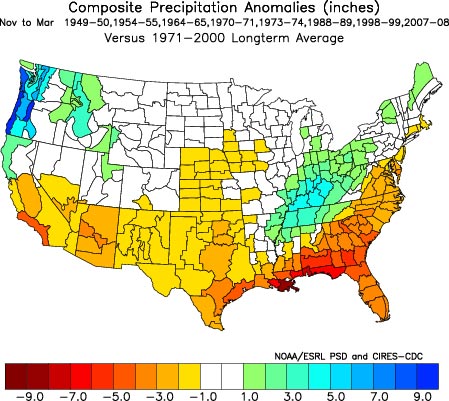
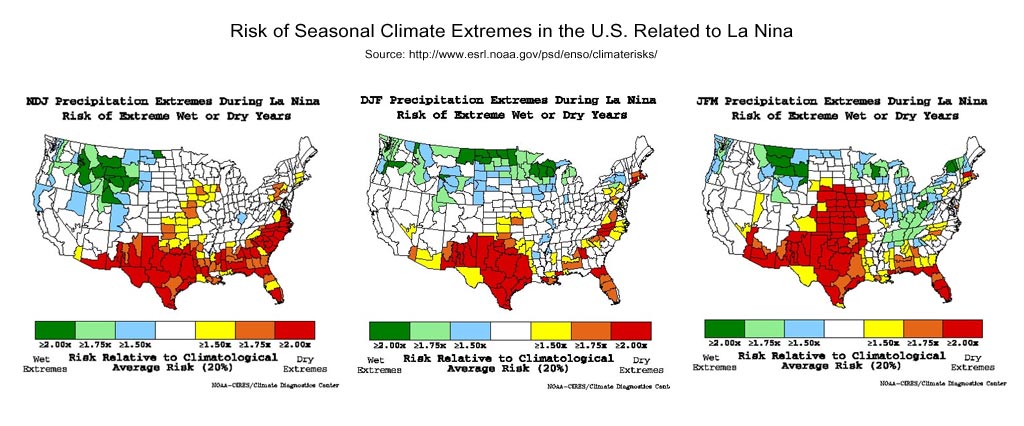
Note: The rain from this storm pushed the water year rainfall total for Downtown Los Angeles to above the 100% mark. Although this might seem unusual in a La Nina influenced rain season, during two of the strongest La Ninas in the past 60 years — 1955-56 and 1973-74 — Los Angeles recorded 99% and 106% of normal rainfall.