
Somewhere around the junction of the 210 and 605 I saw a flash of lightning to the south. As if the flash had been a warning, a gust of wind buffeted my car, and a blizzard of dust and debris blew across the freeway. Then it started to rain. Not good — especially when you’re on your way to a race that ends on top of a 10,000′ mountain.
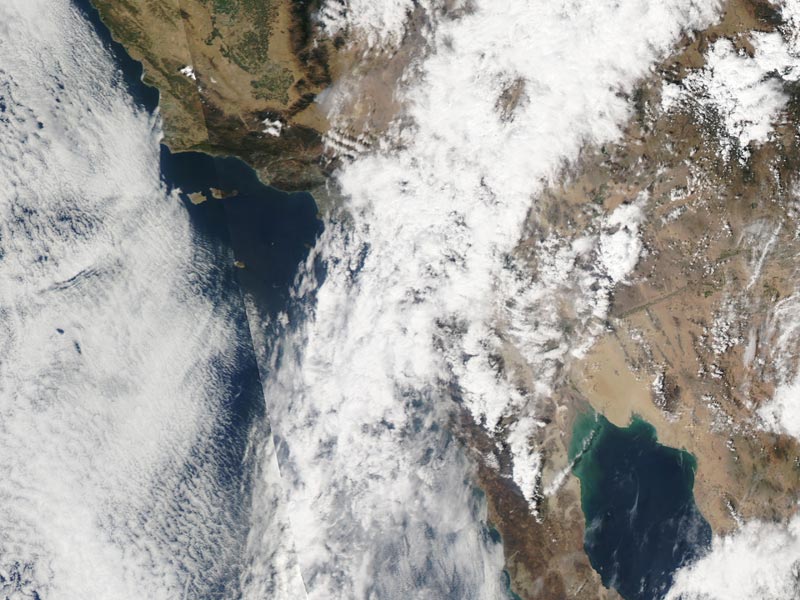

A complicated weather scenario had developed for race day. A very moist layer of monsoonal moisture had been pushed up into Southern California from Baja by a combination of a weak upper level trough off the coast and big upper level high over Four Corners. A combination of factors including an unseasonably strong jet stream had helped trigger a band of showers and thunderstorms that extended from west-southwest off the coast, across the Los Angeles basin, and into the San Gabriel Mountains.
When I drove into the Mt. Baldy Ski Lifts parking lot at around 6:45 am it was raining hard enough I didn’t want to get out of the car. Procrastinating, I went through the admittedly optimistic ritual of applying sun screen. After a few minutes the rain tapered off to sprinkles and I walked down to the Start Line to pick up my bib. The word was conditions were improving and it looked like we were going to be able to get in the race.
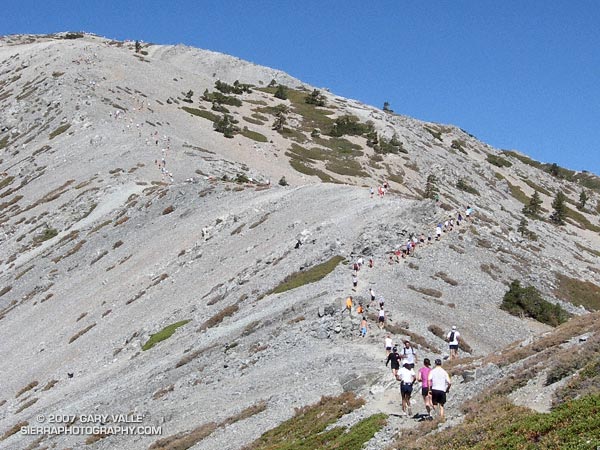

Each year the Baldy Run to the Top attracts 500 to 600 runners. Some are the best of the best and will run the seven miles and nearly 4000′ of elevation gain in under 75 minutes. About two-thirds of the runners usually finish in around 2:15 or less.. A few just want to give it a go and soon find that climbing the rough equivalent of 6500 stairs — at altitude — is more than they bargained for.
Usually the weather is pretty good — some years are a little warmer or cooler, or have a few more clouds than others, but blue skies and sunshine are the norm, and significant rain — or lightning — usually isn’t a problem.
It was deceivingly warm as runners gathered at the start line. The wind chill on top was reported to be a chilly 38 degrees. A few runners had on extra clothing, and a number of runners had an extra top or shell tied around their waste. Some had extra gear stuffed in their packs, but a few — including a couple of shirtless runners — had nothing to combat the weather.
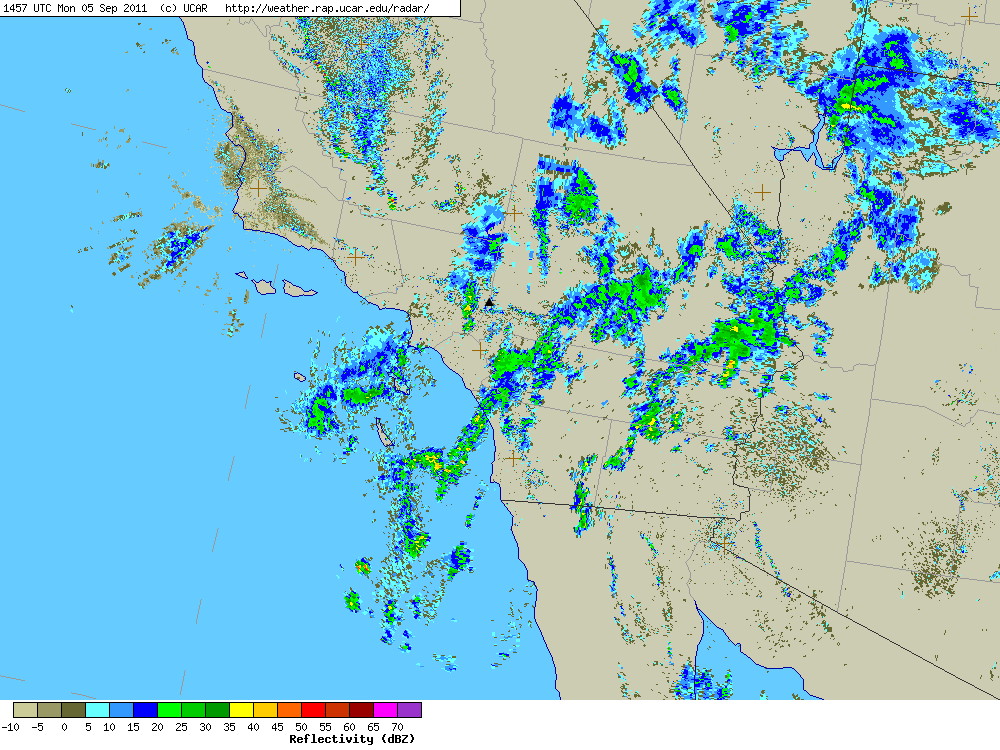
Here’s a UCAR regional NEXRAD composite radar image from about 8:00 am. The approximate location of Mt. Baldy is marked by a black triangle near the center of the image. (Note that radars in the region vary in how they show a particular area and that a cell may be stronger than indicated in the composite. Also there’s some “clutter” in the image that isn’t necessarily rain.)
With what sounded like a more reserved “3… 2… 1… GO!” the race started and pounded down the wet pavement to Manker Flats (6160′), where it turned up the ski area service road. The (mostly) dirt road would take us to the Notch (7800′) and then the top of Chair 4 (8600′). From there a trail would take us across the exposed Devil’s Backbone, then across the south face of Mt. Harwood, and on to the final gut-wrenching 700′ climb to the summit of Mt. Baldy (10,064′). Here’s an interactive Cesium browser View of the race course.
The weather on the way up to the Notch was a little unsettled, but great for running. There was a mix of clouds and sun, and even a brief shower, but overall it looked like the weather might be improving.
Just before rounding the last switchback up to the Notch, a runner with a bib was running down. This was odd because he was running well. Why would he have quit the race? Running up to the aid station at the Notch I still hadn’t caught on, and was wondering why so many people were standing around at the aid station.
That’s when I learned that about 45 minutes into the race, on the recommendation of SAR officials, the race had been shut down. I’m not sure what the “final straw” was but would guess it was nearby thunderstorms and perhaps a growing concern that rain and wind associated with a rapidly developing cell could cause serious problems for runners not prepared for inclement weather.
Here’s what a regional composite radar image looked like at around 9:00 am, and then just one hour later, as a “train” of cells about 20 miles from Mt. Baldy continued to develop and stream into the San Bernardino Mountains in the area of Silverwood Lake, Crestline and Lake Arrowhead.
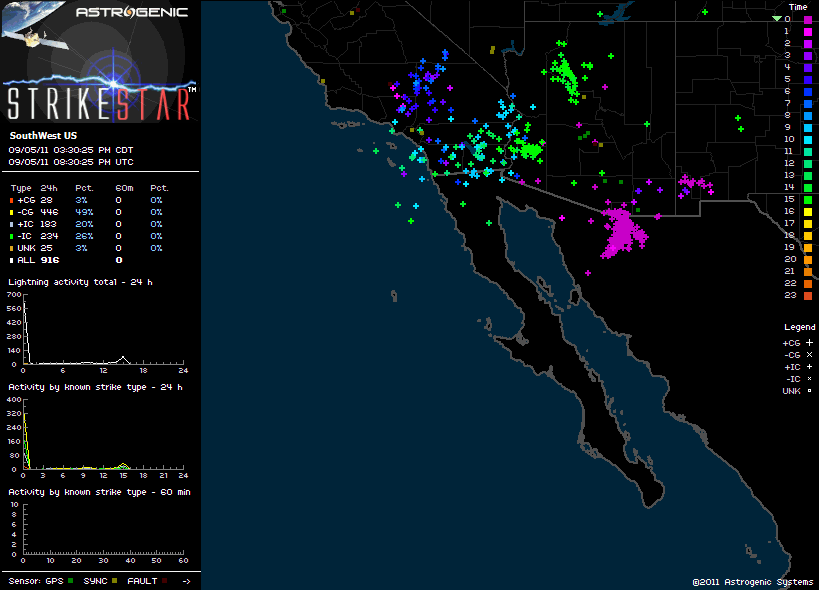
Lightning was not only a risk for runners, but for the 50+ SAR and fire personnel spread across the mountain, and the 25+ volunteers that would be on top of the mountain for the duration of the event.
There was lightning in the area. We saw it driving to the race and I heard at least one clap of thunder while warming up before the race. Here’s an image of Astrogenic StrikeStar lightning detections in the southwestern U.S. from 10:00 pm PDT Sunday to about 1:30 pm PDT race day. Note the high percentage of cloud-ground strokes.
As this composite radar loop from WSI Intellicast.com shows, bands of showers and thunderstorms streamed into the San Gabriel and San Bernardino Mountains most of Labor Day. Cells were moving relatively rapidly and developing over a wide swath that extended from west of Mt. Baldy south and east to San Diego and Palm Springs. (Mt. Baldy is just north of ONT on the radar map.)
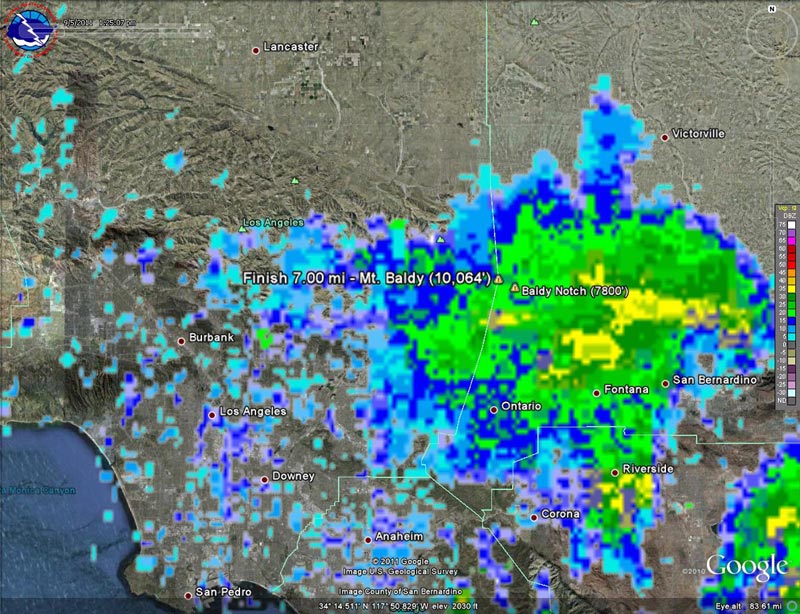
It was pretty much a crapshoot where a particular cell would develop, how strong it would be, and what its extent would be. This regional radar image shows a cell that moved into the Baldy area around 1:00 pm, and this Google Earth/NEXRAD image shows the same cell in relation to Mt. Baldy at around 1:30 pm.
As frustrated as I was to stop at the Notch, I don’t think there’s any question that officials made the right decision when they shut down the race. And I think most runners understand that it’s not whether a particular runner was able to make it up to the summit and back down OK, but what could have happened with several hundred people on the mountain and an ever-so-slight change in that wavering stream of heavy showers and thunderstorms.
Some related posts: Thunderstorm, Mt. Baldy Run to the Top 2009, Mt. Baldy Run to the Top 2007
