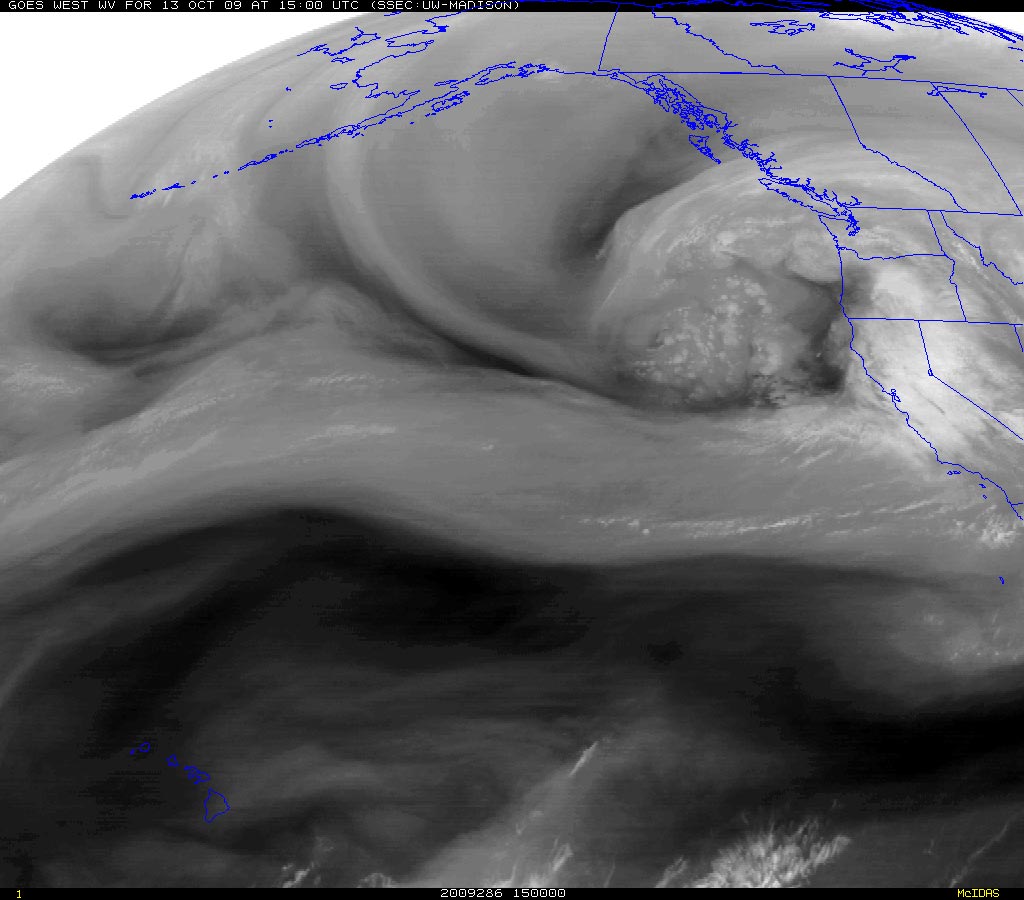
Who would think a western Pacific typhoon could so directly affect California’s weather? But that’s what is happening. The moisture from typhoon Melor, which was over Japan just a few days ago, was captured by an extending and strengthening jet stream. This has resulted in an atmospheric river of moisture, stretching across the Pacific and into California.
This morning, Intellicast composite radar shows Northern and Central California already being hammered by the system. Southern California has seen a few showers, and several stations have already recorded significant rainfall. As of 9:00 a.m. the CNRFC Precipitation Map shows isolated 24 hr. rainfall amounts in the foothills and mountains of Santa Barbara, Ventura, and Los Angeles County ranging from about 0.16 inch at Sandberg to 0.61 inch at West Big Pine.
The last day there was measurable rainfall at Downtown Los Angeles (USC) was on June 5, 2009, when 0.13 inch was recorded. Computer weather models forecast the best dynamics and highest rainfall totals will be in the northern two-thirds of the state, but in recent days have been trending wetter in the Los Angeles area, particularly in the mountains.
With so much moisture in the atmosphere, it takes very little lift to produce rain. Onshore winds, full of moisture, are lifted by foothills and mountains across the flow, and the result is rain — sometimes lots of it. In this case it appears the south to west facing mountains and foothills of Santa Barbara, Ventura and Los Angeles counties may record much higher rainfall totals than the lowland areas.
In a decade characterized by unusual El Ninos, the ongoing El Niño of 2009-2010 is another strange one. El Niño signals continue mixed. The Aug-Sep Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI), decreased from 0.978 to 0.754, however other El Niño signals appear to be rebounding. In the last two weeks low level equatorial westerly anomalies have increased significantly. The reduction in the strength of the trade winds, and a downwelling Kelvin wave resulting from a very strong westerly wind burst already appear to be increasing upper ocean heat content in the central equatorial Pacific. The 30 day moving Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) has been dropping, and should return to negative territory in a day or so.
Recurring equatorial westerly wind bursts and enhanced west-central Pacific convection has been slowly migrating eastward. The most recent round of enhanced convection was centered at about 160E. This is consistent with a developing El Niño, and may have contributed to the creation of the atmospheric river now affecting California, by helping to extend the Pacific jet stream following an East Asian mountain torque event.
However, total and relative AAM remain negative, and are lower than is generally the case during a developing El Niño. Of the weak to moderate El Ninos that have occurred Since 1959, only the 1977-78 and 1994-95 El Niños have had negative average July-September relative AAM values comparable to the current El Niño. Since 1959, only 4 of 15 El Niños have had negative average relative AAM values during the Southern California rain season of November to March. (Revised 12/14/09)
Moderate El Niños come in many flavors and have varying impacts. Under the guise of such El Niños Los Angeles experienced its second wettest water year on record in 2004-2005, when 37.25 inches of rain was recorded; then in 2006-2007 had its driest water year on record, when only 3.21″ was recorded. What flavor will the 2009-2010 El Niño be?
The photo of the tree and clouds is from yesterday’s run at Ahmanson Ranch.
Related post: How Does the El Nino of 2009-10 Compare to Other Warm ENSO Episodes Since 1950?









