
From a run in the Simi Hills earlier in the week.

From a run in the Simi Hills earlier in the week.

I wasn’t familiar with the routes on Ladyface, and wasn’t certain I could get to the peak directly from the Heartbreak Ridge trail. But that’s part of the fun of an adventure run. I had a general idea of what I wanted to do — an out and back from the Phantom trailhead in Malibu Creek State Park to the top of Ladyface. And I had an idea of the time available to do it — about four hours. The details would sort themselves out along the way.
Or at least that was the theory. It was now three in the afternoon, and I was one hour and 56 minutes into sorting out those details. Theoretically, I was supposed to be on the summit of Ladyface in about four minutes.

Earlier, I had run out of trail descending Heartbreak Ridge, and had used a network of coyote paths to get down to Cornell & Kanan roads. But then I chosen the wrong “trail” to start the climb of the peak.
For sure the route would follow one of the prominent ridges on the east side of the mountain. Since the descent of Heartbreak Ridge left me on the northeast side of the peak I had looked for a route there. One car was parked at the start of a dirt road, and a street vendor had indicated he’d seen people start the climb there. My thought was that maybe an established trail would work up the canyon and onto the northeast ridge.
Wrong Charlie Brown! The trail, which (ha!) turned out to be a freeride course, was a dead end. Following it burned about 10 minutes and a good chunk of elevation gain. I ran down and jumped up onto the northeast ridge, where I found a use trail.
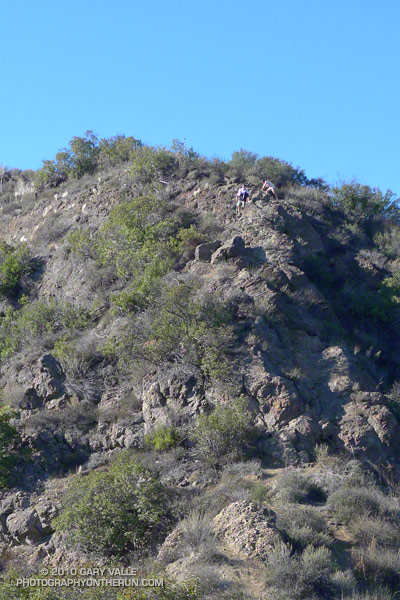

Low on the ridge it looked like this trail might go to a subsidiary peak and not the true summit of Ladyface. Whatever it did, I was now short on time, and committed to this approach. I would follow it until either I ran out of time, or reached a summit.
The face was deep in shadow and wet from Friday night’s rain. Still a couple hundred vertical feet below its top, I zig-zagged up through the steep outcrops of Conejo volcanic rock. It wasn’t how I had pictured the trail on Ladyface, and I hadn’t expected to be climbing on wet, mossy holds for the second weekend in a row.
Two hours and 3 minutes into the adventure I scrambled onto the summit. A surprised hiker asked, “Where did you come from?” I explained, and he commented, “I’ve never climbed Ladyface that way.”
I jogged down the well-used, but somewhat manky trail on the east/southeast ridge, followed Kanan back to Cornell Rd., climbed back up Heartbreak Ridge, and made it back to the car a couple of minutes after five o’clock.

From Sunday’s climb and run over Boney Mountain to Sandstone Peak.

The face was not steep, but I was glad the pockmarked volcanic rock had big holds. Rainwater filled some of the pockets, and patches of lichen and moss on the face were saturated and slippery. It wasn’t a runout climb at the Needles or Tuolumne Meadows, but gravity still worked the same way. I reminded myself not to do something “stoopid.”

At the top of the face I looked around and sighed, and then looked around and sighed again. It was another stunning morning on the western ridge of Boney Mountain. To the west a nearly full moon struggled to remain above the hills, its brightness veiled in a mix of clouds. Another storm was expected in the evening, and the sky told of its approach. Broad strokes of cirrus brushed the blue above, and here and there fingers of tattered stratus reached into the coastal canyons and clung to the wet hillsides.
Today’s forecast for the Santa Monica National Recreation Area had called for mostly cloudy skies, and a high in the 60s. At the moment it was mostly sunny, but already there were hints of clouds developing on the ridges and mountaintops. At some point in the day the clouds would envelop the mountains, and transform the morning’s expansive vistas into a dimensionless gray. I hoped to get up the ridge, over Tri-Peaks, and to Sandstone Peak before that happened.

By chance the clouds behaved, and the splendid views and weather continued all the way to Sandstone Peak, and beyond. The run back to the Wendy Drive trailhead on the Backbone, Sycamore Canyon, and Upper Sycamore trails could not have been better.
As I climbed the final little hill to the parking area I noticed I had no shadow. Over the course of the afternoon the cloud deck would continue to lower and thicken, and by evening light rain would begin across the area.
Some related posts: Clouds and Crags, Conejo Valley Sun and Boney Mountain Clouds, Sandstone Peak from Wendy Drive

The second of two vigorous upper level lows to batter Southern California this Autumn has pushed the water year rainfall totals for many stations around the area to above normal. Does that mean we’re likely to see the wet weather continue through the 2010-2011 rain season?
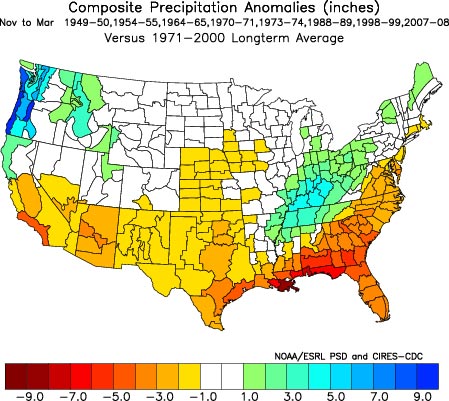
Probably not. Since last Winter, ENSO conditions in the equatorial Pacific have flip-flopped. The Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI) has plunged from the fifth strongest El Nino for Feb/Mar to the strongest La Nina for Aug/Sep. The Aug/Sep value of the MEI is the lowest since Jul/Aug of 1955. Generally, El Nino conditions result in wetter weather in Southern California, and La Nina drier.
A precipitation composite for eight years in which ENSO was transitioning from El Nino or Neutral conditions to La Nina indicates that “on average” the coastal Southern California climate division recorded about 4 to 5 inches less precipitation than normal for the period November through March. The percent of normal water year rainfall recorded at Downtown Los Angeles (USC) ranged from a low of 53% (1988, 8.08″), to a high of 99% (1973, 14.92″). The average rainfall for these years was 77%, or 11.7″.
Maps generated using the ESRL/PSD page Risk of Seasonal Climate Extremes in the U.S. Related to ENSO do not indicate a higher than normal risk for an extremely dry rain season in Southern California when La Nina conditions are present.
La Nina composites from CPC’s ENSO Temperature & Precipitation Composites page suggest the period Jan-Feb-Mar may be particularly dry, but this is not reflected in CPC’s official seasonal precipitation forecasts.
CPC’s Three-Month Precipitation Outlooks and NOAA Winter Outlook were updated yesterday. The precipitation outlook for Nov-Dec-Feb in the Coastal Southern California climate division shows equal chances of above average, near average, or below average precipitation. As the rain season progresses, these probabilities become only slightly skewed toward below normal precipitation. The skew becomes more pronounced in Feb-Mar-Apr when the probability of below normal precipitation increases to 45%.
The title photograph is from Sunday’s out and back run from Chatsworth Reservoir to Rocky Peak.
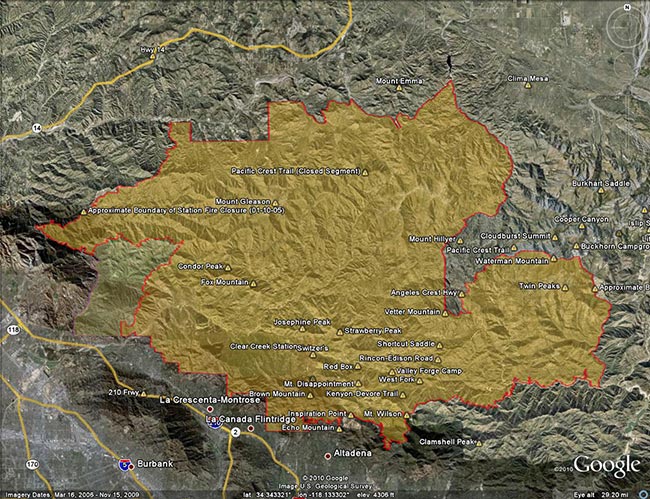
Update Friday, May 13, 2011. Good news! Effective Monday, May 16, 2011, Angeles National Forest is reopening about half of the area of the Forest currently closed as a result of the Station Fire. This reduces the closure area from 186,318 acres to 88,411 acres, and opens most of the burn area south and east of Angeles Crest Highway (Hwy 2) from Bear Canyon east to Twin Peaks. Some of the trails and areas opened are the Sunset Ridge Trail, Bear Canyon Trail, segments of the Gabrielino Trail, Nature’s Canteen Trail, San Gabriel Peak and Mt. Disappointment, Valley Forge Trail, Kenyon DeVore Trail, Silver Moccasin Trail, Pacific Crest Trail (some rerouting), Twin Peaks and the Mt. Waterman-Twin Peaks Trail from Three Points. For more information see the news release, detailed map, and other information related to Closure Order No. 01-11-03 on the Angeles National Forest web site.
On September 20th, after issuing a press release with the title, “Angeles National Forest reopens areas offering hiking, picnicking,” Angeles National Forest (ANF) reopened about 5 percent of the Station Fire closure area, and extended the closure of the remaining 186,320 acres another year to September 19, 2011. Here’s an ANF map of the revised closure area (PDF).
According to the press release, most of the areas burned in the Station Fire remain closed “for public safety.” When will these areas reopen? In the press release former ANF forest supervisor Jody Noiron states, “The Forest Service intent is to reopen areas severely damaged in the fire over the next few years as conditions allow.”
It’s hard to understand the rationale for the extent and duration of this closure. Over the past year, many dedicated forest users have participated in permitted work parties and events in the closure area. We’ve been on the trails and roads. We know firsthand that many miles of trails and dirt roads are passable, and much of the closure area could reasonably be in use.
Remarkably, a year after the fire, the size of the Station Fire closure area remains LARGER than the area burned by the fire! Some areas in the Forest that were burned are open, and some large areas that did not burn are closed.
Other than the boilerplate “to protect natural resources and provide for public safety” in the closure order, and some bureaucratic arm-waving, there has been very little information released documenting why these areas of ANF should remain closed.
According to an article posted on the Pasadena Star News web site (08/22/10 by Beige Luciano-Adams), acting ANF forest supervisor Marty Dumpis said, “It’s not just safety but also we have to allow the area to recover because if we allow people to start trampling over regrowth then they’ve just set it back another year. We hope people will be patient enough, allow natural recovery to begin, and then we can get some of these areas open.”
Is that the way Angeles National Forest higher-ups see us? The hikers, runners, and riders that most frequently use these trails are among the most experienced that visit the Forest. Trails constrain use, and are a minuscule part of the recovery area. If credible evidence exists that trail use would delay the area’s fire recovery, Angeles National Forest should make it available to the public.
To keep such a large area of public land closed for such an extended period following a Southern California fire is unprecedented. Even in the case of the largest Southern California fires, the Cedar and Zaca fires, closed areas in Cleveland and Los Padres National Forests were reopened within a year of the fire. In many cases fire closures in the National Forests of California have been lifted within days or weeks of a large fire. This reflects a general policy that closures be implemented and maintained as a last resort.
In a 2009 presentation following the Station Fire, Jody Noiren noted that Angeles National Forest:
– provides 72% of all open space in Los Angeles County
– has 17 million people living and working within 1 hour drive
– has 3.5 million visitors per year, of which half come from within a 50 mile radius of the Forest
It may simplify forest management, and be more convenient for the Forest Service to keep such a large area of Angeles National Forest closed, but it is clearly not in the public interest. Extending the Station Fire closure will not enhance recovery, increase protection of sensitive species, or prevent the spread of invasive plants. But it will deprive millions of people living and working nearby of an indispensable and intrinsic public resource.
Long experience in Southern California demonstrates that public lands can be reopened in a timely fashion following a fire without abusing resources, or putting the public in undue peril. It is time to stop the doublespeak and reopen all but the most severely damaged areas of the Station Fire burn area to public use.
The Station Fire closure area is in the congressional districts of Rep. David Dreier [R-CA26] and Rep. Howard McKeon [R-CA25]. California’s senators are Sen. Barbara Boxer [D-CA] and Sen. Dianne Feinstein [D-CA]. Determine and contact your Representative and Senators.