Originally posted January 7, 2016 and rewritten to reflect the current rainfall totals for Downtown Los Angeles. Rain season totals have been updated as of March 31.
Based on 1981-2010 climate normals Downtown Los Angeles (USC) receives, on average, 1.04 inches of rain in November, 2.33 inches of rain in December, and 3. 12 inches in January. This past November Los Angeles recorded only 0.01 inch of rain, and in December only 0.57 inch. January rainfall was a few hundredths above normal at 3.17 inches.
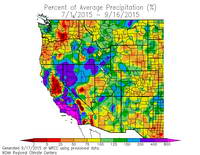
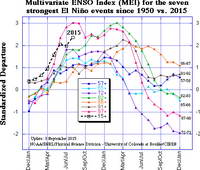
The 2015-16 El Nino is one of the three strongest El Ninos in the past 65 years; the other two were 1982-83 and 1997-98. How does the amount of rain we’ve had so far this rainfall year compare to the other two? Is this El Nino failing to produce the expected amount of rainfall in Los Angeles?
On January 7, when this post was originally written, the rain year totals were in the same ballpark for the date as during the 1982-83 and 1997-98 El Ninos. That is no longer the case, and Los Angeles rainfall totals are falling far behind those other big El Ninos.
As of January 31 Downtown Los Angeles (USC) has recorded only 6.97 inches of rain for this rain year, which is 0.47 inch below normal. At this point during the 1982-83 El Nino Los Angeles had already recorded 12.98 inches of rain, and in the 1997-98 El Nino 9.15 inches. (See updates below.)
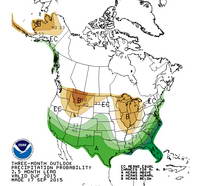
The good news is that the Sierra snowpack is above average. That helps with the water supply, but not so much with naturally-occurring local groundwater and other drought impacts in Southern California. It does help that the Los Angeles rain year total is nearly normal, but I’m still waiting to see running water in upper Las Virgenes Creek.
Remarkably, as of this morning, the medium range models are forecasting dry weather to predominate over the next 10 days or so and both the GFS and ECMWF show a mega-ridge of high pressure developing over the West Coast this weekend. We’ll see!
Update:
As of March 31 Downtown Los Angeles (USC) has recorded only 9.36 inches of rain for 2015-16 rain year, which is 68.5% of normal. At this point during the 1982-83 El Nino Los Angeles had already recorded 25.72 inches of rain, and in the 1997-98 El Nino 26.89 inches. All the data for the April 1 Sierra Snow Course Measurements are not available yet, but it looks like the snowpack will be around 85% of normal. In 1983 the weighted statewide average snowpack was 227% of normal and in 1998 it was 158% of normal.