
Incense cedar on the Burkhart Trail in Cooper Canyon. From Sunday’s Three Points loop.

Incense cedar on the Burkhart Trail in Cooper Canyon. From Sunday’s Three Points loop.
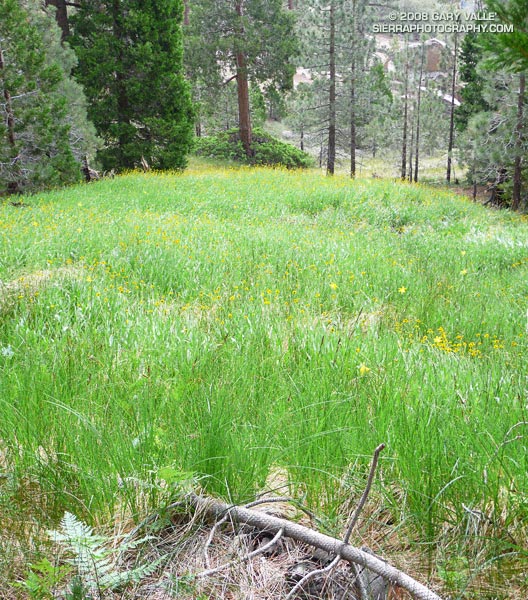

Lemon lilies and sneezeweed accent this lush mountain meadow on the south side of Waterman Mountain in the San Gabriel Mountains. From Sunday’s Three Points loop, just before it started to rain.

If you spend much time in the mountains, sooner or later you’re going to get caught in a severe thunderstorm. I don’t mean you’re going to hear a little thunder and get a little wet. I mean you’re going to find yourself in the middle of a heart-pounding, ear-splitting, ozone-smelling, sense-numbing storm that drenches you through and through and wrings the nerves from your body.
Having been caught in such thunderstorms while climbing in Yosemite, running in the San Gabriels, and running at Mt. Pinos, I do my best to avoid the beasts. Sometimes, it is not an easy thing to do.
Take this weekend for example. I have a 50K race coming up, and in addition to increasing my weekday mileage, I needed to do a Sunday run of about 20-25 miles — preferably in the mountains.
The Sierra was out. A monsoon pattern virtually assured widespread, and possibly severe, thunderstorms. Some forecast models were saying that the focus on Sunday might be the Ventura County mountains, so Mt. Pinos — the site of my most recent thunderstorm adventure — was also out. Both San Gorgonio and San Jacinto had been hit pretty hard on Saturday. That left the San Gabriels, and thunderstorm activity was expected there as well.
The choices were A — get up really early and try to beat the heat and humidity and run local; or B — get up really early and try to get in a mountain run before the weather OD’d…
Running up the Mt. Waterman Trail, one of my ever-optimistic running partners voiced, “Hey, have you heard about the unusual number of lightning deaths recently?” So far it had been a spectacular day. A broken layer of mid-level clouds — remnants of yesterday’s storms — shrouded the sky. By keeping things a little cooler, the clouds had delayed the development of today’s thunderstorms.
We had started at Three Points and run up the Pacific Crest Trail to Cloudburst Summit, then down into Cooper Canyon, where we left the PCT and ascended the Burkhart Trail to Buckhorn Campground. In Cooper Canyon it was obvious there had been heavy rain the day before. Everything was wet, and the willows and lupines along the creek glistened in the muted morning sun. Rivulets of rainwater had incised rills in the trail, pushing pine needles and other debris into patterned waves.
I had already lost the “when it would start raining” bet. I had said 11:00. It was 11:00 now, and still there was very little cloud development. So little in fact, we decided to do a quick side trip to Mt. Waterman (8038′), and jokes were being made about the rain gear in my pack. (My GoLite 3 oz shell made a huge difference in the severe thunderstorm on Mt. Pinos.)
About the time we summited Waterman, things started to cook. The canopy of protective clouds was beginning to thin and dissipate and some cumulus cells were starting to build. I wondered if we would make it back to the car before it dumped.
We didn’t. About 30 minutes later, as we worked down the back side of Mt. Waterman toward the junction with the Twin Peaks trail, we heard our first grumbling of thunder. In another 30 minutes it started to rain; slowly at first, with large icy drops, then building in intensity, as prescribed in long established thunderstorm protocols. Periodic claps of thunder echoed overhead, and to the north and east.
About 3 or 4 miles of trail remained. Here, the trail winds in and out of side-canyons and for the most part is well below the main ridge, but at some points it is very exposed. Minutes before, we had run past a lightning scarred Jeffrey Pine. Burned and blackened, the bolt had killed the tree. I pick up the pace and try to put the tree out of mind.
It rained hard for a while and then the intensity diminished. The air temperature didn’t drop and the wind wasn’t strong. It seems most of the lightning is cloud-to-cloud and away from us. I’m drenched, but happy — instead of being fierce and frightful, this thunderstorm has been almost puffy-cloud friendly.
In steady rain, we cross Hwy 2 and jog up the trail toward the Three Points parking lot (5920′). As we near our cars, we’re startled by a loud boom of thunder directly over our heads — a not so gentle reminder that thunderstorms come in all sizes, and none come with a guarantee.
Here’s a Google Earth image and Google Earth KMZ file of the loop, including the side trip to the summit of Mt. Waterman.
Some related posts: Manzanita Morning, Three Points – Mt. Waterman Loop
Introduced around 2000, the Garmin eTrex was the first GPS unit I used to trace a trail run. The GPS tracks were imported into TOPO! where the length of a run could be measured, an elevation profile generated, and the topography of the run examined.
Since the eTrex was designed to be used in an “orienteering” position — flat in your hand in front of your body — it would frequently have trouble receiving GPS satellite signals if hand-carried while running or hiking. About the time enterprising hikers and runners began to resolve this issue with creative hats, holsters and harnesses, Garmin released the Forerunner 201, greatly simplifying the task of tracing a route.
In 2005, while preparing a presentation about kayaking Piru Creek for a meeting with the Forest Service, I stumbled onto Keyhole.com. To say I was blown away by this bit of “Eureka” technology would be an a gross understatement. Now, in addition to seeing Piru Creek in photographs, and on a topo map, you could get a “before you paddle” preview using Keyhole — even if you couldn’t paddle class IV whitewater! Google acquired Keyhole in late 2004 and launched Google Earth on June 28, 2005.
Shortly after Google Earth was launched, SportTracks added the ability to launch Google Earth and view the GPS trace of a run or other activity. Since SportTracks could also directly import data from Garmin’s Forerunner, the software made it very easy to view a run in Google Earth.
I’ve been working on updating the posts on Photography on the Run that reference a trail run to include a link to a Google Earth KMZ file. A KMZ file is just a zipped KML file, and either can be opened in Google Earth. A list of the trail runs with KMZ file links can be found by clicking “Google Earth KMZ Files of Trail Runs” in the sidebar.
These are actual tracks recorded by a GPS during a trail run and may contain GPS errors, route-finding errors, and wanderings that are difficult to explain. In a few instances tracks have been modified to correct errors, or to remove side excursions that are not part of the usual route, but not all errors have been corrected. No claim is being made regarding the appropriateness or suitability of the routes indicated.

It isn’t unusual for snow to persist on New Army Pass (12,300′) well into July. Strong northwest winds, following in the wake of blustery Winter storms, blow freshly fallen snow over the crest and into this cirque, forming cornices along its lip, and dense slabs of wind-ground snow in it’s lee.
That’s why the July 1 Sequoia & Kings Canyon National Park Trail Conditions report for New Army Pass seemed plausible. It read, “The top of the pass has an 30 foot snow wall – ice axe recommended.”
The reported trail conditions are a compilation of reports from the field, and are not always up-to-date. Having been over the pass a number of times, and in a variety of conditions, I thought that we would probably be able to bypass any remaining patches of snow without needing an ice axe. Worst case, if the pass looked dicey, we could use Cirque Peak or some other alternative route to attain the crest.
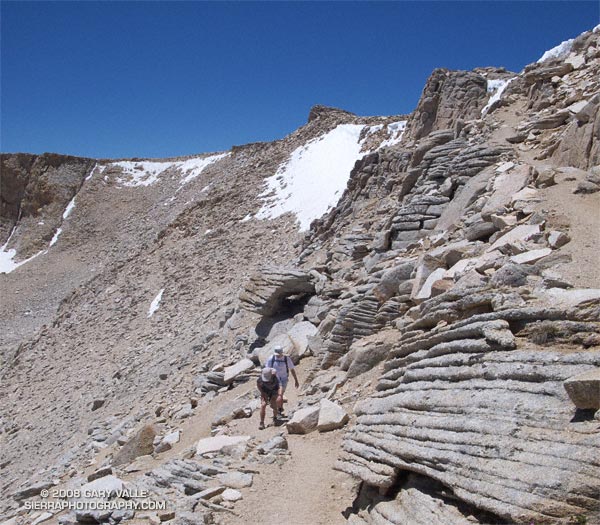

We need not have worried. While there was snow in the cirque, and in a couple of places along the trail near the top of the pass, the trail was completely clear. Even so, it was a good excuse to do the 21 mile Cottonwood loop counterclockwise — the reverse of my usual circuit — climbing up New Army Pass from the Cottonwood Lakes side, and then running down into Rock Creek basin.
Now that I’ve done the loop in both directions, I think I prefer the clockwise circuit. The 9 miles of running from New Army Pass down through the Cottonwood Lakes basin is generally better than the running down from Chicken Spring Lake and Cottonwood Pass. Also, there’s more downhill on some sandy sections of trail between Chicken Spring Lake and Rock Creek. The tradeoff is you give up the nice downhill into Rock Creek basin, and near the end of the loop have a mile or so of annoying uphill.
Here’s a Google Earth image, Google Earth KMZ file, and an elevation profile of a GPS trace of the route. (The elevation profile was generated using SportTracks.)
Related posts: Cottonwood – New Army Pass Loop, Mt. Langley in a Day from L.A.

We were making good progress up the gargantuan north face of University Peak (13,632′), climbing carefully and doing our best not to knock loose rocks down on each other’s heads. We were also doing our best to ignore the gathering clouds — and the unnerving rumble of distant thunder.
Yes, it would have been better to sleep at the trailhead and get an early start. Especially with a 20% chance of isolated thunderstorms in the forecast. But we didn’t. When we should have been taking our first steps on the Kearsarge Pass trail we were eating breakfast burritos in Mojave. So it goes.
Now we were about half way up the 2200′ class 2-3 face, and it would take another hour of climbing to reach the summit. That would put us on the summit right around the time of maximum daytime heating — a bad time to top out if you’re trying to avoid a thunderstorm.
Off to the northwest there was another long, rolling, rumble of thunder. Streamers of rain could be seen twining from darkening clouds. Smoke from one or more of California’s many fires hung in the valleys to the west of the crest, producing an unnatural and eerie mixture of clouds, smoke, rain, and orange tinted terrain.
We paused in a jumble of broken blocks of granite, hemming and hawing, and otherwise hesitating to make THE decision to descend. Avoiding the issue and pondering the sky, we wondered which fire the smoke was coming from, and — half in jest — whether the smoke could have seeded and enhanced the thunderstorm we were watching. Those questions, it turns out, had surprising answers.
I had assumed the smoke was from one of the fires to the west. But this NRL Aqua-MODIS True Color satellite photo from 1:38 in the afternoon reveals the source of the smoke — it was from the Piute Fire between Lake Isabella and Tehachapi. The long plume of smoke from this fire feeds almost directly north into the large thunderstorm cluster near 37N and -118.5W.
From our vantage point on University Peak, the southern margin of this activity appeared to be about 6 miles away, somewhere near Gardiner Basin. This experimental NRL image shows the convection more clearly. Could this smoke plume have enhanced the storms over the Sierra?
The research article “Smoking Rain Clouds over the Amazon” by M. O. Andreae, et al, published in Science Magazine in 2004, and related research, suggests the possibility. According to that article, vegetation burning produces high concentrations of aerosols which are capable of nucleating cloud droplets. But, convective clouds forming in smoky air show substantially reduced droplet size compared to similar clouds in clean air. The reduced droplet size can delay the onset of precipitation, which in turn can result in enhanced convection.
So why blame the thunderstorm on Cristina? This NRL water vapor satellite photo from 3:30 p.m. suggests that the source of the moisture for the Sierra thunderstorms was Tropical Storm Cristina. An upper level low spinning off the coast had drawn the moisture up from the tropics and into the Sierra.
Related post: Thunderstorm, Shadow and Sun on University Peak (The north face is highlighted by the sun.)