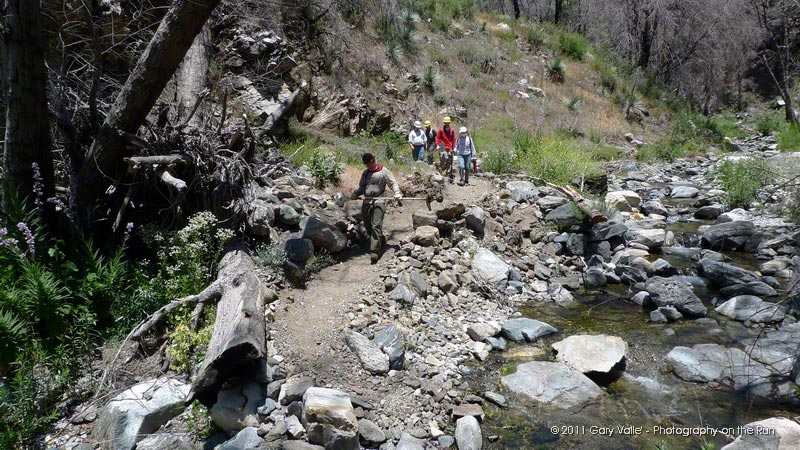
Runners on Edison Road During a Recent Training Run
Note: The Mt. Disappointment Endurance Run is now the Angeles National Forest Trail Race.
No matter if you run at the front, middle, or back of the pack, there’s the race you plan, and the race you run.
Based on the course info, it looked like the 7th edition of the Mt. Disappointment 50K was going to be more difficult than in 2009 and 2010, adding both mileage and elevation gain. Because of the closure of Mueller Tunnel and the damage done by the Station Fire and subsequent floods, we still wouldn’t be running up and over the shoulder of Mt. Disappointment, or down to Clear Creek and around Strawberry Peak, but the 2011 course would make up for that with its own very memorable sections.
To try and cope with the difficulties of the course, I’d put in extra miles and done more back to back Saturday-Sunday runs. But in one of those uh-oh moments a couple of miles into the race, I could feel in my legs that I was probably going to need to adjust my expectations. I wasn’t injured. I wasn’t getting over a cold or flu. My stomach wasn’t upset. I felt pretty good. But there was this nagging bit of fatigue in my legs…
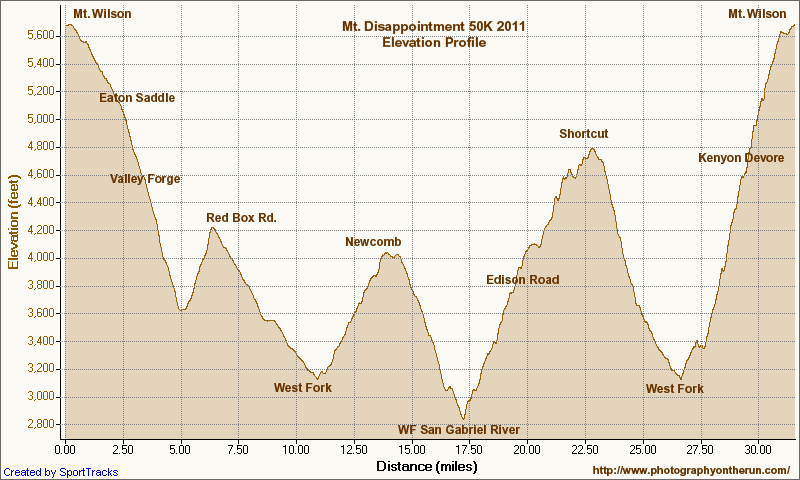
The new wrinkle for 2011 was that we turned off Mt. Wilson Road half-way to Red Box and ran down the Valley Forge Trail. In a training run a few weeks before the race, the Valley Forge Trail had been an obstacle course overgrown with Turricula (Poodle-dog bush). Trail work by Hilliard, Rowlan & Company had restored the trail, and today it was in great shape. Here’s an interactive Cesium browser View of the 2011 course and the courses in previous years, and an elevation profile of the 2011 course.
At the bottom of the Valley Forge we turned onto the Gabrielino Trail, and started up the canyon of the West Fork toward Red Box-Rincon Road. The change in grade from level to uphill confirmed it. I stepped aside so two running friends could pass. Maybe it was a tapering or over-training issue, or maybe it was just “one of those days.” Whatever, the legs were just not cooperating.
The irony is, this was probably a good thing. The day turned out to be the hottest of any Mt. Disappointment race to date. The lurking leg fatigue forced me to not push the pace, which made dealing with the temperature easier.
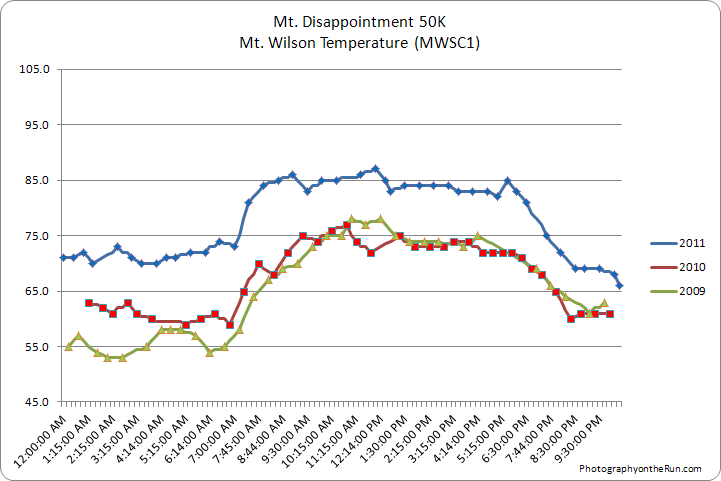
And hot it was! The forecast had looked decent just two days before the race, but Friday temperatures exploded in the mountains, jumping 10-12 degrees in 24 hours. The hot temps on Friday carried over into Saturday, making race day just that much warmer.
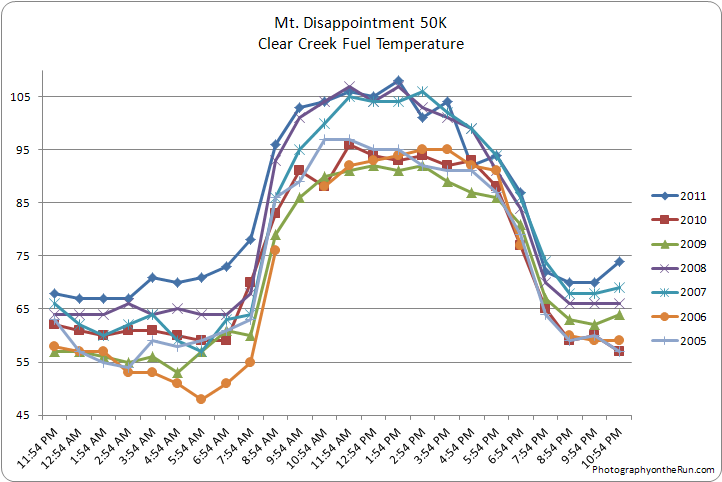
Here are the race day temperatures at Clear Creek and Chilao for 2005-2011, and Mt. Wilson for 2009-2011. And these temps are the temperature off the ground and in the shade! A better indication of the temperature in the sun is the “fuel temperature.” This is the temperature of a ponderosa pine dowel in direct sun. Here are plots of the race day fuel temperature at Clear Creek and Chilao for 2005-2011.
Because I wasn’t pushing the pace I didn’t hesitate to take a little extra time at aid stations. I can still feel that ice cold sponge on the back of my neck, and the cold water running down my back. This year there were numerous small stream crossings, and I think there was at least one small stream between every aid station. This was “free” cooling, and I paused a dozen times to dump water over my head. Thanks to the West Fork San Gabriel River, I was soaked from head to toe for the first steep, sun-baked section of Edison Road. This was also the case on the Silver Moccasin Trail in Shortcut Canyon and on part of Kenyon Devore.
Hot day or not there were some remarkable performances. Heather Fuhr was not only was the first place woman, she was fourth overall and set a new women’s course record of 5:07:11. Perennial favorite Jorge Pacheco sped through the tough Mt. Disappointment course in 4:46:29, winning the overall and setting a new course record in the Men’s 40-49 Division.
Once again the event was superbly organized by race director Gary Hilliard and the Mt. Disappointment 50K Staff, with the help of an extraordinary group of volunteers, runners, SAR personnel and sponsors. Thank you!
Related post: Mt. Disappointment 50K 2010 Notes














