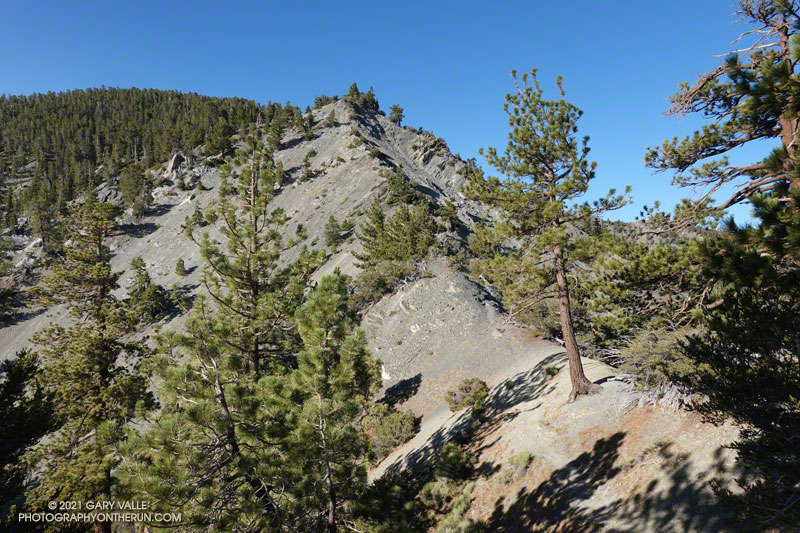
The last time I was on this part of the North Backbone Trail it was bitterly cold and very windy. Today it was just very windy. Even though the air temperature was in the 70s, the “wind chill” was enough that I was considering grabbing the sleeves and shell from my pack.
I stopped in the lee of a sprawling, stunted lodgepole pine and enjoyed a moment of relief, shielded from the wind. But there wasn’t that much mountain above me, and I resumed zig-zagging up the final steep stretch of trail. Climbing a little higher, I could see the trail sign that marks the top of the North Backbone Trail.

Mt. Baldy from Wrightwood is a more difficult variation of the North Backbone Trail route. Instead of driving to the North Backbone Trailhead on East Blue Ridge Road (F.R. 3N06), you run/hike to the trailhead using the Acorn Trail and a short stretch of Blue Ridge Road or the PCT. (The dirt road is slightly shorter, but you don’t have to dodge off-road vehicles when on the PCT.)
Including Pine Mountain (9648′) and a short detour to the top of Dawson Peak (9575′), the regular North Backbone route is about 8 miles long and gains/loses around 4700′. Starting in Wrightwood at the small parking area on Acorn Drive ups those totals to around 15 miles, with a 6800′ gain/loss.

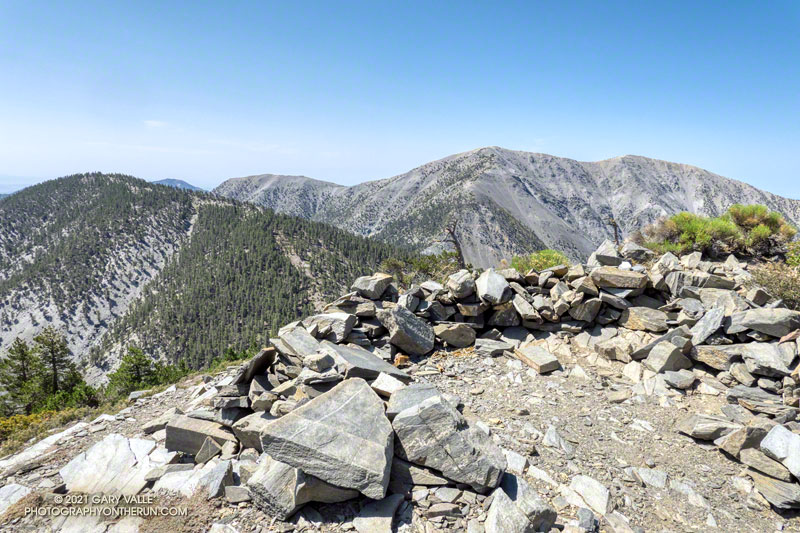
A mix of hikers and trail runners were scattered across the broad summit of Mt. Baldy (10,064′). The wind wasn’t as strong on the summit as it had been on the North Backbone. Smoke from the Western wildfires reduced the visibility, but the air quality and view were still pretty good.
Like many mountains, the adventure didn’t end on the top of the peak. The elevation gain on the way back to Wrightwood is significant, and much of the downhill demands close attention — especially on tired legs. I squeezed the water bladder in my pack and tried to estimate how much was left. The day was just going to get warmer, and I hoped it was enough to get me back over Dawson Peak and Pine Mountain. On the way up, I’d stashed a small water bottle near the North Backbone Trailhead, and that would help on the final few miles.

Other than initially running past my water stash, the descent went well. Once on the PCT I could run normally — well, more or less normally — and it didn’t take long to get over to the Acorn Trail.
When doing the AC100 and related training runs, I’d run/hiked up the Acorn Trail a number of times, but I’d never run down it. After all the rough trail on the North Backbone, it was great to be able to cruise down through a forest of pine and fir on a well-groomed trail! Here’s an elevation profile of the route.
Explore the scenery and terrain of this out-and-back trail run and hike from Wrightwood to Mt. Baldy using our high resolution, interactive, 3D viewer. The imagery is so detailed, it’s almost like being there! To change the view, use the control on the upper right side of the screen, the CTRL key and your mouse, or touch gestures. Track and placename locations are approximate and subject to errors. Snow, ice, poor weather, and other conditions may make this route unsuitable for this activity.
Some related posts: Mt. Baldy North Backbone Trail, North Backbone Trail Revisited, Mt. Baldy Run Over the Top, Inspiration Point to the Pine Mountain Juniper and Pine Mountain